JOURNAL ARTICLES:
-
1. S. Tao, Y. Minami and M. Ishikawa: “Performance evaluation of ORB-SLAM3 with quantized images”, Artif. Life Robotics, Vol. 30, No. 2, 2025.
CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS:
-
1. S. Tao, Y. Minami, M. Ishikawa: “Assessing the Impact of Dynamic Image Quantization based on Error Diffusion on Visual SLAM”, Proc. of 29th Int’l Symp. on Artificial Life and Robotics, Japan, 2024.
-
2. S. Tao, Y. Minami, M. Ishikawa: “Memory-Saving Factor Analysis of Visual-Inertial SLAM with Quantized Images”, SICE Festival 2024 with Annual Conference, Japan, 2024.
-
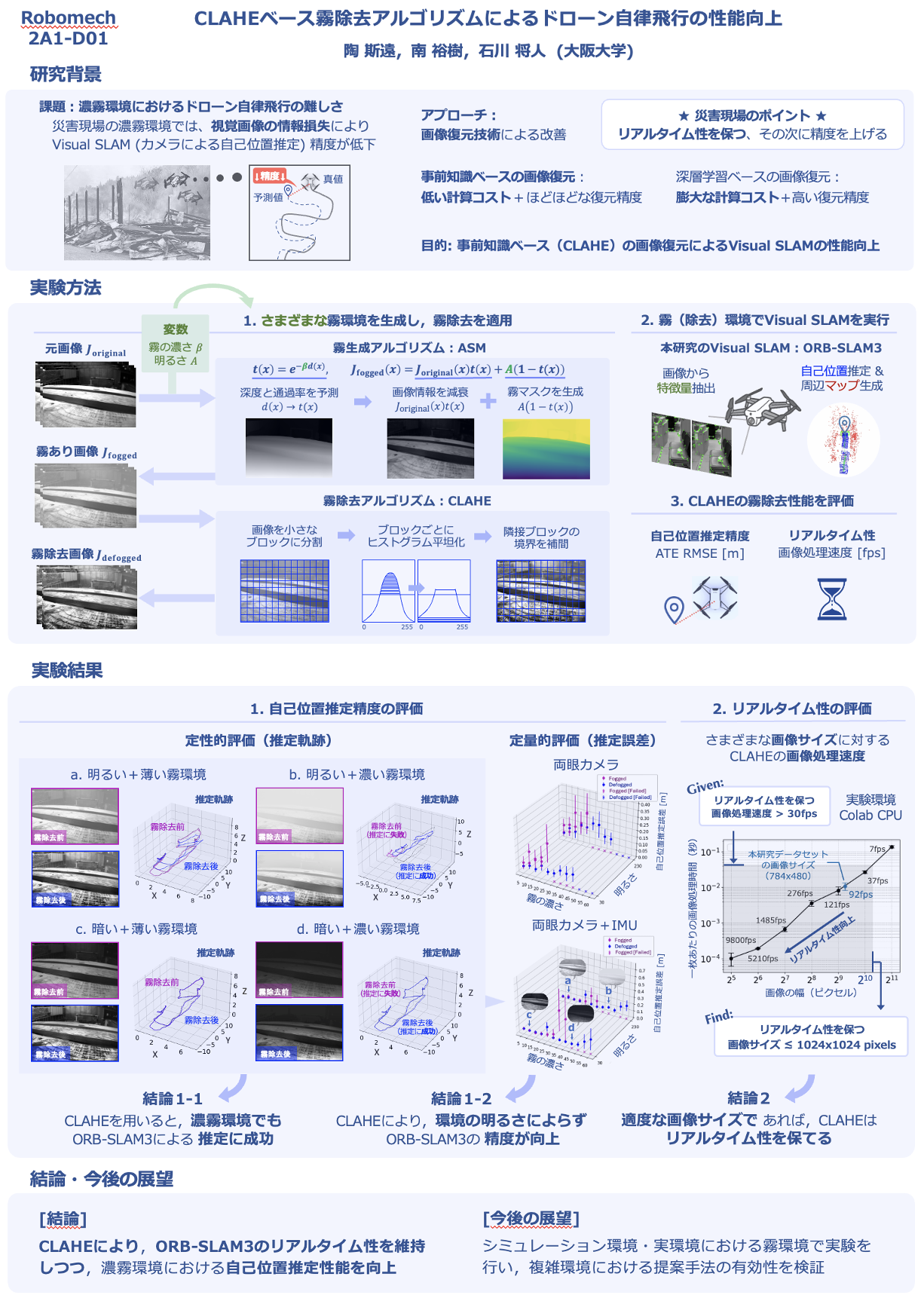
3. S. Tao, Y. Minami, M. Ishikawa: Performance Enhancement in Autonomous Drone with CLAHE-based Fog Removal Algorithm, Robomech Conference, Japan, 2025.
-
4. A. Michikawa, S. Tao, Y. Masuda, M. Gunji, A. Fukuhara, H. Nabae, Y. Harada, K. Suzumori. Deep Biomimetic Printing Enabling Integration and Composite Fabrication of Tendon-Ligament-Skeletal Structure, Robomech Conference, Japan, 2025.
-
5. A. Michikawa, S. Tao, Y. Masuda, M. Gunji, A. Fukuhara, H. Nabae, Y. Harada, K. Suzumori: “Deep Biomimetic Printing using Fiber Embedding and Sponge Ossification”, International Symposium on Adaptive Motion of Animals and Machines (AMAM2025), Germany, 2025.
AWARDS:
-
1. Received an award for excellence in university-wide education(大阪大学全学教育優秀賞), 2020.
-
2. Awarded the Special Prize at the NHK Robot Contest(Robocon), 2021.
-
3. Won a bronze medal in a Kaggle competition: "Google AI4Code - Understand Code in Python Notebooks", 2022.
-
4. Received the Hatakeyama Award(畠山賞) from the Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2024.
CERTIFICATIONS:
-
1. TOEFL iBT: 99 (2022.6)
-
2. TOEIC Reading&Listening: 860 (2022.7), 855 (2025.3)
-
3. Passed the JDLA Deep Learning for GENERAL(G検定) 2024#3 certification. (2024.3)
-
4. Completed the Large Language Model Course 2024(大規模モデル講座2024) organized by Matsuo-Iwasawa Lab in the University of Tokyo, 2024.
-
5. Completed the World Model Course 2024(世界モデル講座2024) organized by Matsuo-Iwasawa Lab in the University of Tokyo, 2025.
-
6. Completed the AI Business Insight Course 2025(AI経営講座2025) organized by Matsuo-Iwasawa Lab in the University of Tokyo, 2025.
-
7. Completed the Deep Generative Model Course 2025(深層生成モデル2025) organized by Matsuo-Iwasawa Lab in the University of Tokyo, 2025.
OTHER ACHIEVEMENTS:
-
1. Exempted from the graduate school entrance examination due to excellent undergraduate academic performance, 2023.
-
2. Selected as a scholarship recipient by the Kajima Ikueikai Foundation(鹿島育英会), 2024.
-
3. S. Tao, K. Konno, K. Takaoka: “Assessment of the Relationship Between Intelligence Scaling and Task Efficiency in Embodied Multi-Agent Systems with LLMs”, poster presentation for the World Model Course 2024 at Sanjo Conference Hall, The University of Tokyo, Japan, 2025.
-
4. Employed as a Research Assistant (RA) under the JST Fusion Oriented Research for disruptive Science and Technology Program, 2025.